Table of Links
III. Dead Reckoning using Radar Odometry
IV. Stochastic Cloning Indirect Extended Kalman Filter
IV. STOCHASTIC CLONING INDIRECT EXTENDED KALMAN FILTER
A. State Augmentation
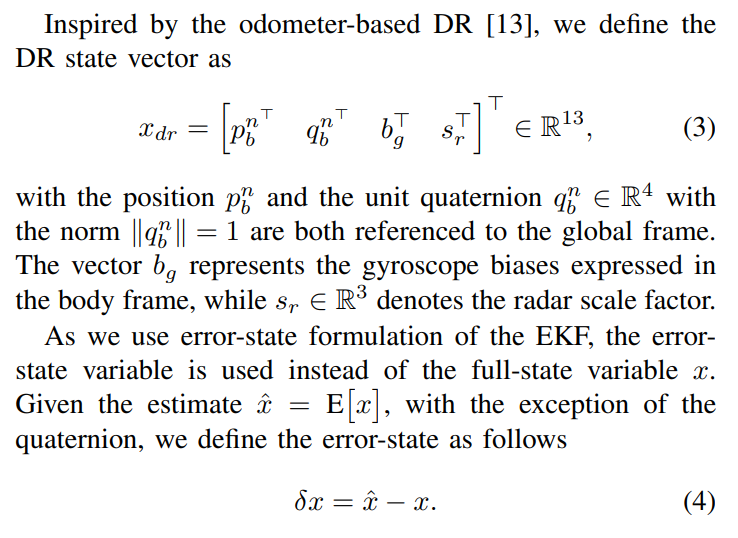

B. System Model
We now define the mathematical model of the gyroscope and radar sensors a

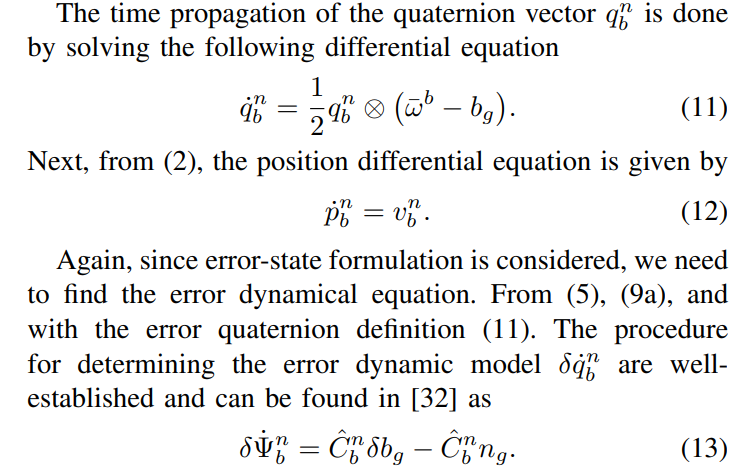


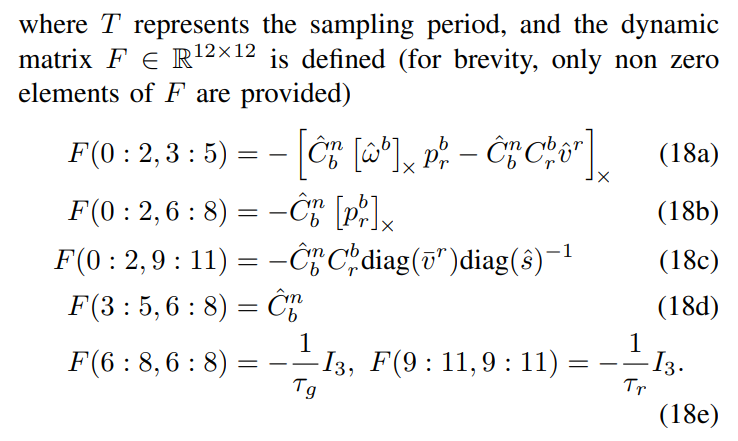
The augmented transition matrix is then given by
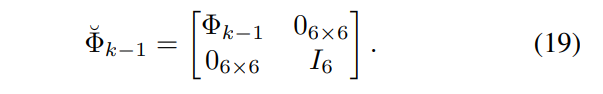
As a result, the error covariance of the augmented system is propagated as [28]

C. Measurement Model
Model The DeRO system leverages measurement from both radar (distance of the targets) and tilt angles calculated from accelerometers. We shall describe each measurement model in detail
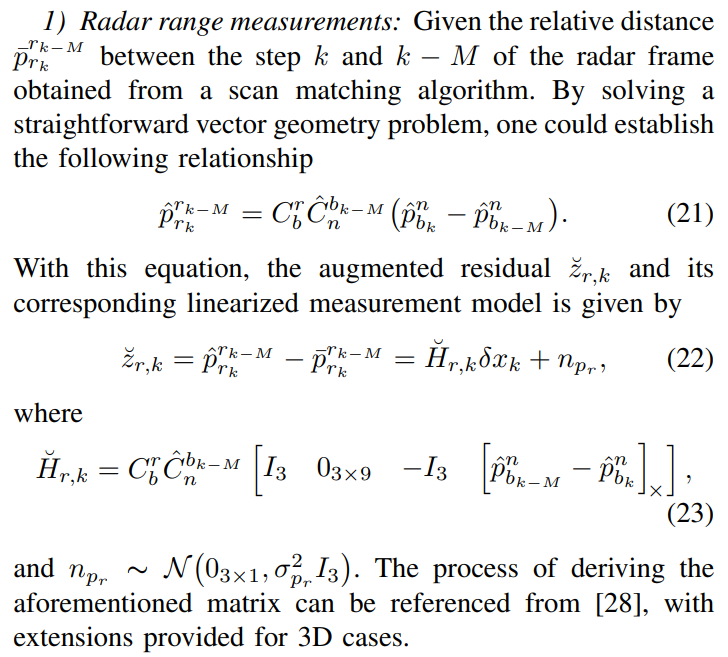
D cases. Unlike in [29], where each target’s distance measurement is directly used, we employ the entire scan for matching to determine the distance between frames. This strategy leads to a significant reduction in computation

According to the relationship between Euler angles and misalignment angles [21], we establish the following linearized measurement model to update the DR estimation

D. Implementation
on The detailed step-by-step practical implementation of the DeRO is outlined in Algorithm 1. In our approach, the procedure for each sensor is executed as soon as the corresponding sensor’s data becomes available.
:::info
Authors:
(1) Hoang Viet Do, Intelligent Navigation and Control Systems Laboratory (iNCSL), School of Intelligent Mechatronics Engineering, and the Department of Convergence Engineering for Intelligent Drone, Sejong University, Seoul 05006, Republic Of Korea (hoangvietdo@sju.ac.kr);
(2) Yong Hun Kim, Intelligent Navigation and Control Systems Laboratory (iNCSL), School of Intelligent Mechatronics Engineering, and the Department of Convergence Engineering for Intelligent Drone, Sejong University, Seoul 05006, Republic Of Korea (yhkim@sju.ac.kr);
(3) Joo Han Lee, Intelligent Navigation and Control Systems Laboratory (iNCSL), School of Intelligent Mechatronics Engineering, and the Department of Convergence Engineering for Intelligent Drone, Sejong University, Seoul 05006, Republic Of Korea (dlwngks12@sju.ac.kr);
(4) Min Ho Lee, Intelligent Navigation and Control Systems Laboratory (iNCSL), School of Intelligent Mechatronics Engineering, and the Department of Convergence Engineering for Intelligent Drone, Sejong University, Seoul 05006, Republic Of Korea (mhleee@sju.ac.k)r;
(5) Jin Woo Song, Intelligent Navigation and Control Systems Laboratory (iNCSL), School of Intelligent Mechatronics Engineering, and the Department of Convergence Engineering for Intelligent Drone, Sejong University, Seoul 05006, Republic Of Korea (jwsong@sejong.ac.kr).
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under ATTRIBUTION-NONCOMMERCIAL-NODERIVS 4.0 INTERNATIONAL license.
:::