This guest post was written by Mulay Ahmed and Caroline Lima-Lane of Principal Financial Group. The content and opinions in this post are those of the third-party authors and AWS is not responsible for the content or accuracy of this post.
With US contact centers that handle millions of customer calls annually, Principal Financial Group® wanted to modernize their customer call experience. In the post Principal Financial Group increases Voice Virtual Assistant performance using Genesys, Amazon Lex, and Amazon QuickSight, we discussed the overall Principal Virtual Assistant solution using Genesys Cloud, Amazon Lex V2, multiple AWS services, and a custom reporting and analytics solution using Amazon QuickSight.
This post focuses on the acceleration of the Virtual Assistant (VA) platform delivery processes through automated build, testing, and deployment of an Amazon Lex V2 bot (including other database and analytics resources described later in this post) using a GitHub continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipeline with automated execution of the Amazon Lex V2 Test Workbench for quality assurance. This solution helps Principal® scale and maintain VA implementations with confidence and speed using infrastructure as code (IaC), configuration as code (CaC,) and an automated CI/CD approach instead of testing and deploying the Amazon Lex V2 bot on the AWS Management Console.
Principal is a global financial company with nearly 20,000 employees passionate about improving the wealth and well-being of people and businesses. In business for 145 years, Principal is helping approximately 70 million customers (as of Q4 2024) plan, protect, invest, and retire, while working to support the communities where it does business.The enterprise virtual assistant engineering team at Principal, in collaboration with AWS, used Amazon Lex V2 to implement a voice virtual assistant to provide self-service and routing capabilities for contact center customers. The following engineering opportunities were recognized and prioritized:
- Elimination of console-driven configuration, testing, and deployment of an Amazon Lex V2 bot
- Collaboration through structured version control and parallel development workflows for multiple team members
- Acceleration of development cycles with automated build, test, and deployment processes for Amazon Lex bot creation and optimization
- Enhanced quality assurance controls through automated testing gates and coding standard validation for reliable releases
With the automation solutions described in the post, as of September 2024, Principal has accelerated development efforts by 50% across all environments (development, pilot, and production) through streamlined implementation and deployment processes. This solution also enhances deployment reliability through automated workflows, providing consistent updates while minimizing errors across development, pilot, and production environments, and maximizes development efficiency by integrating the Test Workbench with GitHub, enabling version control and automated testing.With the automation of the Test Workbench and its integration with GitHub, the solution strengthens the CI/CD pipeline by maintaining alignment between test files and bot versions, creating a more agile and reliable development process.
Solution overview
The solution uses the services described in Principal Financial Group increases Voice Virtual Assistant performance using Genesys, Amazon Lex, and Amazon QuickSight. The following services/APIs are also used as part of this solution:
- AWS Step Functions to orchestrate the deployment workflow
- The Test Workbench APIs, which are invoked within the Step Functions state machine as a sequence of tasks
- AWS Lambda to process data to support some of the Test Workbench APIs inputs
VA code organization and management
The Principal VA implementation uses Genesys Cloud as the contact center application and the following AWS services organized as different stacks:
- Bot stack:
- The Amazon Lex V2 CDK is used for defining and deploying the bot infrastructure
- Lambda functions handle the bot logic and manage routing logic (for Amazon Lex and Genesys Cloud)
- AWS Secrets Manager stores secrets for calling downstream systems endpoints
- Testing stack:
- Step Functions orchestrates the testing workflow
- Lambda functions are used in the testing process
- Test files contains test cases and scenarios in Test Workbench format
- Simulated data is used to simulate various scenarios for testing without connecting to downstream systems or APIs
- Data stack:
- Amazon Dynamo DB manages and stores bot prompts
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) stores testing data
- Analytics stack:
- Amazon S3 stores logs and processed data
- Amazon Data Firehose streams logs to Amazon S3
- Lambda orchestrates extract, transform, and load (ETL) operations
- AWS Glue manages the Data Catalog and ETL jobs
- Amazon Athena is used for querying and analyzing analytics data in Amazon S3
- Amazon QuickSight is used for data visualization and business intelligence
- CI/CD pipeline:
- GitHub serves as the source code repository
- A GitHub workflow automates the CI/CD pipeline
Amazon Lex V2 configuration as code and CI/CD workflow
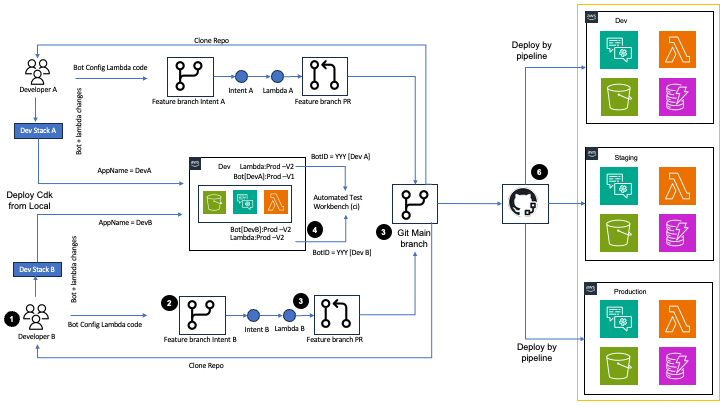
The following diagram illustrates how multiple developers can work on changes to the bot stack and test in parallel by deploying changes locally or using a GitHub workflow.

The process consists of the following steps:
- A developer clones the repository and creates a new branch for changes.
- Developer A or B makes changes to the bot configuration or Lambda functions using code.
- The developer creates a pull request.
- The developer deploys the Amazon Lex V2 CDK stack through one of the following methods:
- Create a pull request and ensure all code quality and standards checks are passing.
- Merge it with the main branch.
- Deploy the Amazon Lex V2 CDK stack from their local environment.
- The developer runs the Test Workbench as part of the CI/CD pipeline or from their local environment using the automation scripts.
- Tests results are displayed in GitHub Actions and the terminal (if run locally).
- The pipeline succeeds only if defined checks such as linting, unit testing, infrastructure testing and integration, and Test Workbench functional testing pass.
- After all tests and checks pass, a new pre-release can be drafted to deploy to the staging environment. After staging deployment and testing (automated and UAT) is successful, a new release can be created for production deployment (after manual review and approval).
Amazon Lex Test Workbench automation
The solution uses GitHub and AWS services, such as Step Functions state machines and Lambda functions, to orchestrate the entire Amazon Lex V2 Bot testing process (instead of using the existing manual testing process for Amazon Lex). The pipeline triggers the upload of test sets, Lambda functions to interact with the Amazon Lex V2 bot and Test Workbench, then another Lambda function to read the tests results and provide results in the pipeline.
To maintain consistent, repeatable evaluations of your Amazon Lex V2 bots, it’s essential to manage and organize your test datasets effectively. The following key practices help keep test sets up-to-date:
- Test set files are version-controlled and linked to each bot and its version
- Separate golden test sets are created for each intent and updated on a regular basis to include production customer utterances, increasing intent recognition rates
- The versioned test data is deployed as part of each bot deployment in non-production environments
The following diagram illustrates the end-to-end automated process for testing Amazon Lex V2 bots after each deployment.

The post-deployment workflow consists of the following steps:
- The developer checks the test file into the GitHub repository (or deploys directly from local). After each bot deployment, GitHub triggers the test script using the GitHub workflow.
- The test scripts upload the test files to an S3 bucket.
- The test script invokes a Step Functions state machine, using a bot name and list of file keys as inputs.
- Amazon Lex Model API calls are invoked to get the bot ID (ListBots) and alias (ListBotAliases).
- Each test file key is iterated within a Map state, where the following tasks are executed:
- Call Amazon Lex APIs to start import jobs:
- StartImport – Creates a test set ID and stores it under an S3 bucket specified location.
- DescribeImport – Checks if the status of StartImport is complete.
- Run the test set:
- StartTestExecution – Creates a test execution ID and executes the test.
- ListTestExecutions – Gathers all test executions. A Lambda function filters out the current test execution id and its status.
- Get test results.
- Call Amazon Lex APIs to start import jobs:
- When the test is complete:
- The ListTestExecutionResultItems API is invoked to gather overall test results.
- The ListTestExecutionResultItems API is invoked to fetch test failure details at the utterance level if present.
- A Lambda function orchestrates the final cleanup and reporting:
- DeleteTestSet cleans up test sets that are no longer needed from an S3 bucket.
- The pipeline outputs the results and if there are test failures, these are listed in the GitHub action or local terminal job report.
- Developers conduct the manual process of reviewing the test result files from the Test Workbench console.
Conclusion
In this post, we presented how Principal accelerated the development, testing, and deployment of Amazon Lex V2 bots and supporting AWS services using code. In addition to the reporting and analytics solution, this provides a robust solution for the continued enhancement and maintenance of the Virtual Assistant ecosystem.
By automating Test Workbench processes and integrating them with version control and CI/CD processes, Principal was able to decrease testing and deployment time, increase test coverage, streamline their development workflows, and deliver quality conversational experience to customers. For a deeper dive into other relevant services, refer to Evaluating Lex V2 bot performance with the Test Workbench.
AWS and Amazon are not affiliates of any company of the Principal Financial Group.
This communication is intended to be educational in nature and is not intended to be taken as a recommendation.
Insurance products issued by Principal National Life Insurance Co (except in NY) and Principal Life Insurance Company. Plan administrative services offered by Principal Life. Principal Funds, Inc. is distributed by Principal Funds Distributor, Inc. Securities offered through Principal Securities, Inc., member SIPC and/or independent broker/dealers. Referenced companies are members of the Principal Financial Group, Des Moines, IA 50392. ©2025 Principal Financial Services, Inc. 4373397-042025
About the authors
Mulay Ahmed is a Solutions Architect at Principal with expertise in architecting complex enterprise-grade solutions, including AWS Cloud implementations.
Caroline Lima-Lane is a Software Engineer at Principal with a vast background in the AWS Cloud space.