Found your Raspberry PI Pico in a cupboard that you opened 2 years before… Get along with this project to make a line follower robot using Raspberry Pi Pico and a few other Stuff
What is a Line Follower Robot?
A line follower is a type of autonomous robot that can detect and follow a line drawn on the floor, typically a black line.
Components Required
| Component | Quantity | Notes |
|—-|—-|—-|
| Raspberry Pi Pico | 1 | Use the Pico H for easier pin access |
| BFD-1000 IR sensor array / any 5 array IR sensor Module | 1 | To detect the Black Line |
| L298N motor driver | 1 | To drive motors precisely |
| BO Motors (3–12V) | 2 | Preferably 12V ones 🙂 |
| Bo motor Wheels | 2 | Wheels For Bo Motor |
| Caster wheel (free wheel) | 1 | To balance the front |
| LiPo Battery (12V) | 1 | Or any regulated 12V source |
| Wires, breadboard, etc. | As needed | For connections |
| Computer | 1 | For programming and debugging |
Cooking the Pi🍳
The Software Part
1. Installing Thonny IDE
-
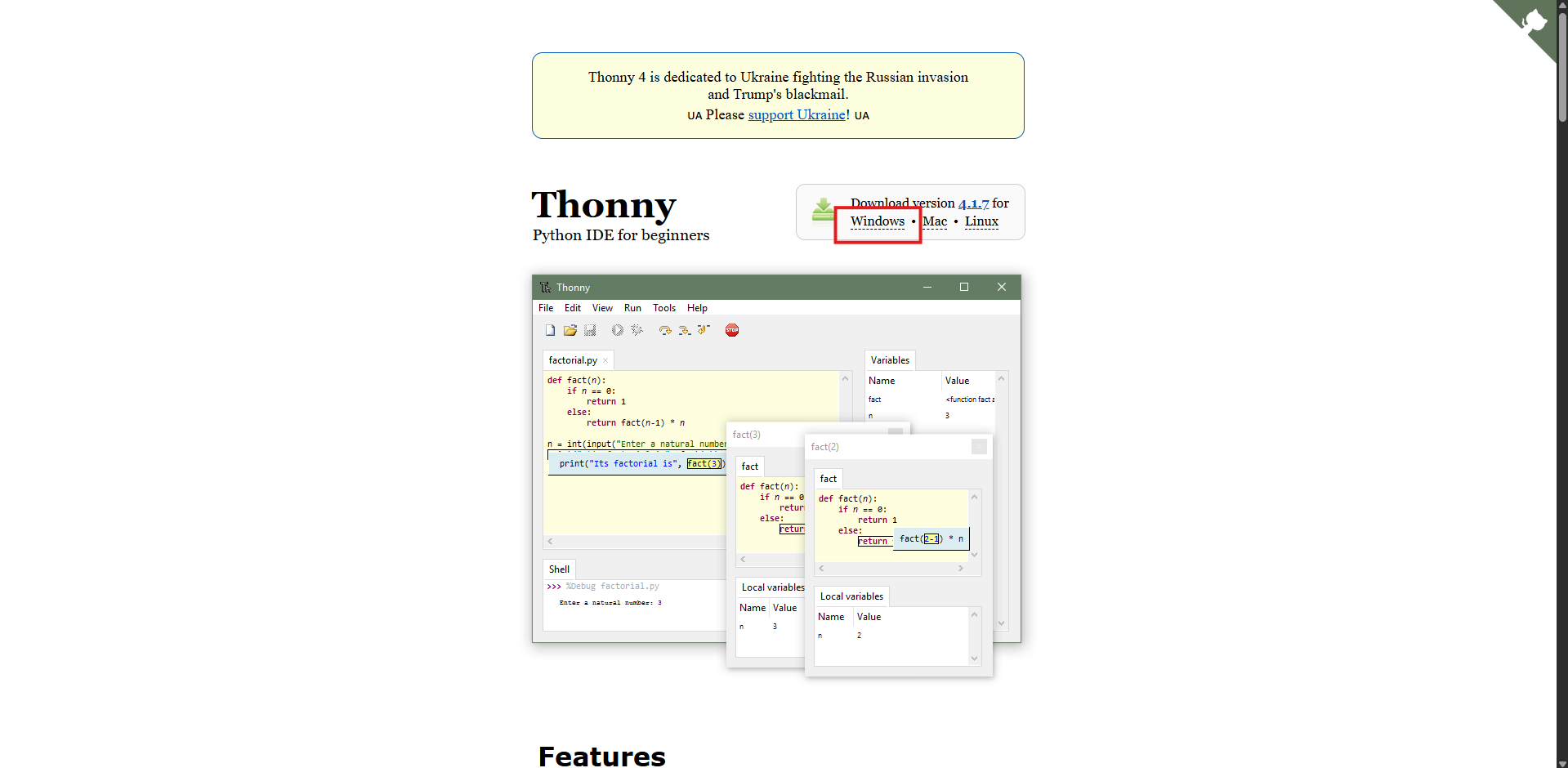
Visit: thonny’s Website
-
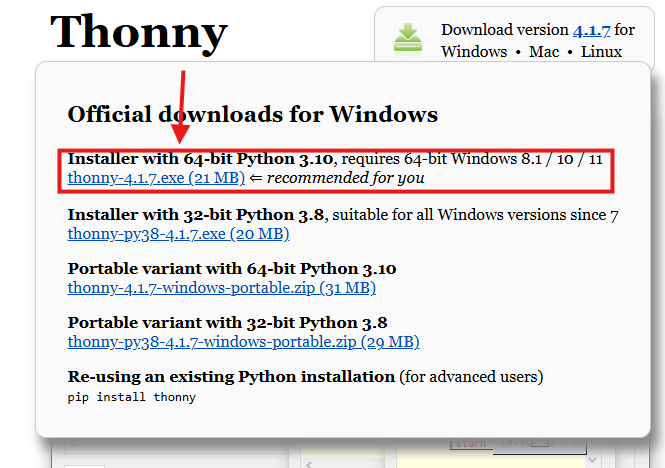
Download it for your OS (Windows/Mac/Linux).
-
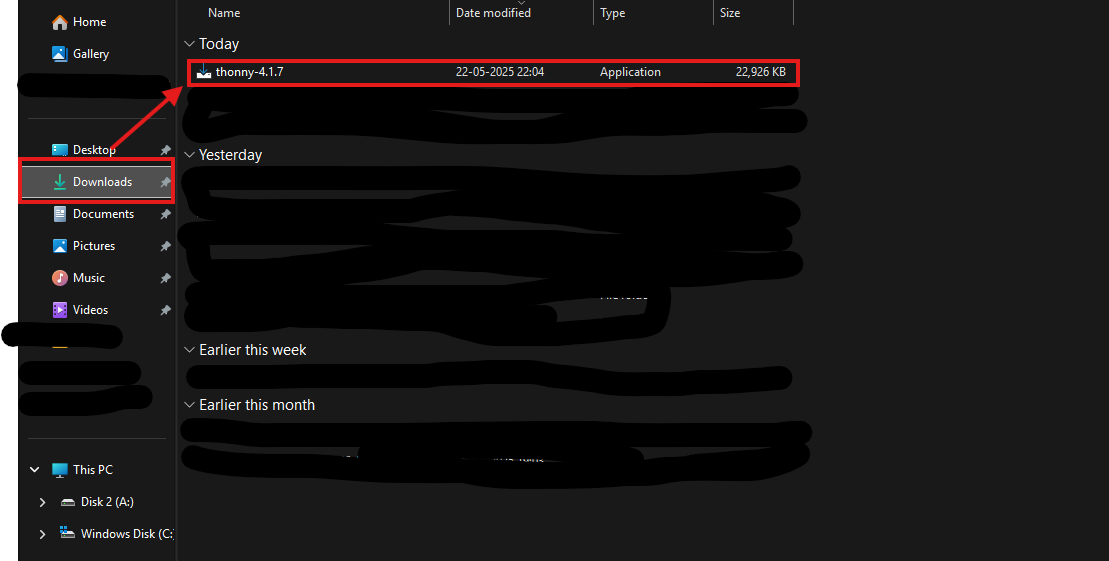
Navigate to the Downloads folder after the .exe file has been downloaded in File Explorer
-
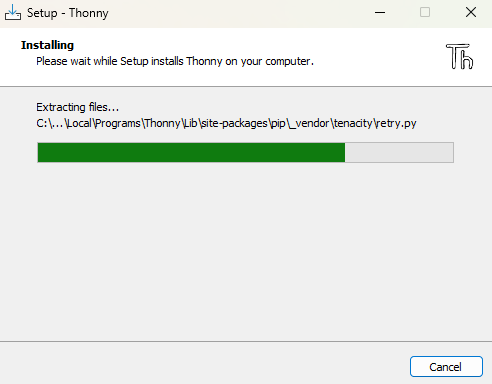
Then click on the .exe file (thonny-4.1.7.exe) to execute the application and click on next until you see that the thonny is being installed
Flashing the pico with Micropython Firmware
:::info
If you have already flashed the micropython firmware the you can skip to next part
:::
Plug in your Pico while holding the BOOTSEL button.
- It appears as a USB drive.
- Go to micropython.
uf2[ file]() download for Pico - Download
.uf2the file and copy it to the Pico USB drive. - Pico will reboot into MicroPython.
Set up Thonny
-
Open Thonny
-
Go to Run > Select Interpreter > MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico)
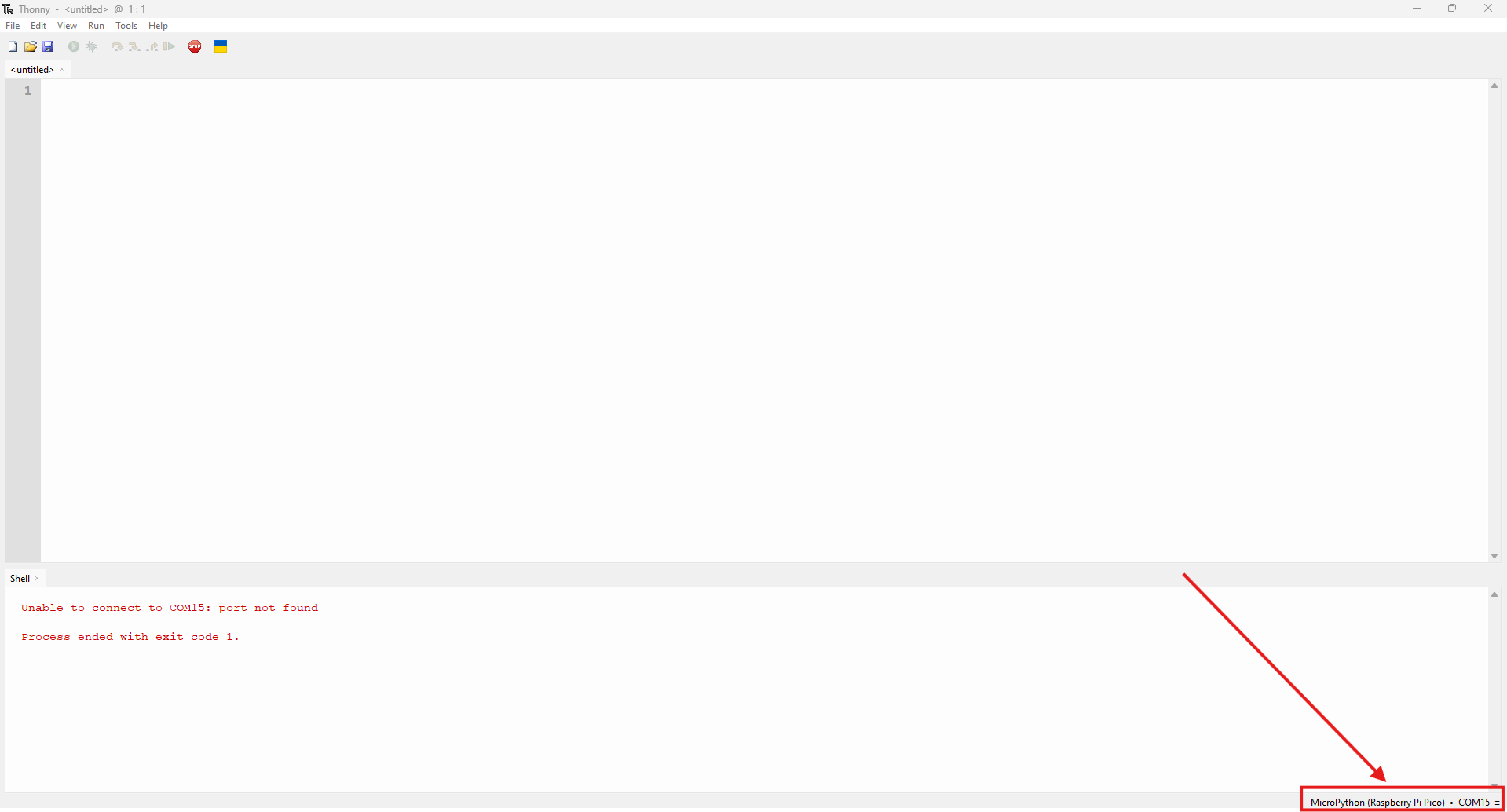
-
Select the right port.
-
Paste the following MicroPython code into the script area
Get code here or paste the code below
from machine import Pin, PWM
import time
# Motor Pins
in1 = Pin(2, Pin.OUT)
in2 = Pin(3, Pin.OUT)
in3 = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
in4 = Pin(5, Pin.OUT)
ena = PWM(Pin(6))
enb = PWM(Pin(7))
ena.freq(1000)
enb.freq(1000)
# Sensor Pins
sensors = [Pin(i, Pin.IN) for i in range(8, 13)]
# Speed Settings
BASE_SPEED = 35000 # Slow and safe for normal movement
MAX_SPEED = 40000 # Max PWM limit
TURN_SPEED = 25000 # Slower speed for turning
# PID Settings
Kp = 8000 # Proportional gain, tune this as per your bot
Ki = 0
Kd = 0
# PID Variables
previous_error = 0
integral = 0
# Motor control functions
def set_motor_speed(left_speed, right_speed):
left_speed = max(0, min(MAX_SPEED, left_speed))
right_speed = max(0, min(MAX_SPEED, right_speed))
if left_speed == 0:
in1.low()
in2.low()
else:
in1.high()
in2.low()
if right_speed == 0:
in3.low()
in4.low()
else:
in3.high()
in4.low()
ena.duty_u16(left_speed)
enb.duty_u16(right_speed)
def stop():
in1.low()
in2.low()
in3.low()
in4.low()
ena.duty_u16(0)
enb.duty_u16(0)
# Read sensor values
def read_sensors():
return [s.value() for s in sensors]
# Calculate position (PID error calculation)
def calculate_error(sensor_values):
weights = [-2, -1, 0, 1, 2]
total = 0
count = 0
for i in range(5):
if sensor_values[i] == 0: # Line detected (assuming black line)
total += weights[i]
count += 1
if count == 0:
return None # Line lost
return total / count
# PID controller
def pid_control(error):
global previous_error, integral
if error is None:
return 0, 0 # No correction needed if line is lost
integral += error
derivative = error - previous_error
correction = int(Kp * error + Ki * integral + Kd * derivative)
previous_error = error
return correction, correction
# Smart Search with PID
def smart_search():
global previous_error, integral # Reset PID variables for search
previous_error = 0
integral = 0
for attempt in range(5):
print("Search attempt", attempt+1)
# Turn left (using PID control)
in1.low()
in2.high()
in3.high()
in4.low()
ena.duty_u16(TURN_SPEED)
enb.duty_u16(TURN_SPEED)
time.sleep(0.5)
stop()
time.sleep(0.1)
sensor_values = read_sensors()
error = calculate_error(sensor_values)
left_correction, right_correction = pid_control(error)
if 0 in sensor_values:
print("Found line after left turn")
return
# Turn right (using PID control)
in1.high()
in2.low()
in3.low()
in4.high()
ena.duty_u16(TURN_SPEED)
enb.duty_u16(TURN_SPEED)
time.sleep(1.0)
stop()
time.sleep(0.1)
sensor_values = read_sensors()
error = calculate_error(sensor_values)
left_correction, right_correction = pid_control(error)
if 0 in sensor_values:
print("Found line after right turn")
return
print("Failed to find line after searching.")
# Main loop
while True:
sensor_values = read_sensors()
print("Sensors:", sensor_values)
error = calculate_error(sensor_values)
if error is None:
print("Line lost, starting search")
stop()
smart_search()
else:
correction = int(Kp * error)
left_speed = BASE_SPEED - correction
right_speed = BASE_SPEED + correction
set_motor_speed(left_speed, right_speed)
time.sleep(0.01)
Click on the save icon 
-
You will get a Prompt stating:-
Where do you want to save
1)Raspberry Pi Pico
2)To this PC
-
Choose Pico and save the file as
main.pyotherwise it will not auto-run on when powered on
The Hardware part
Connections
Here is a link for the line follower connections:- Click Here
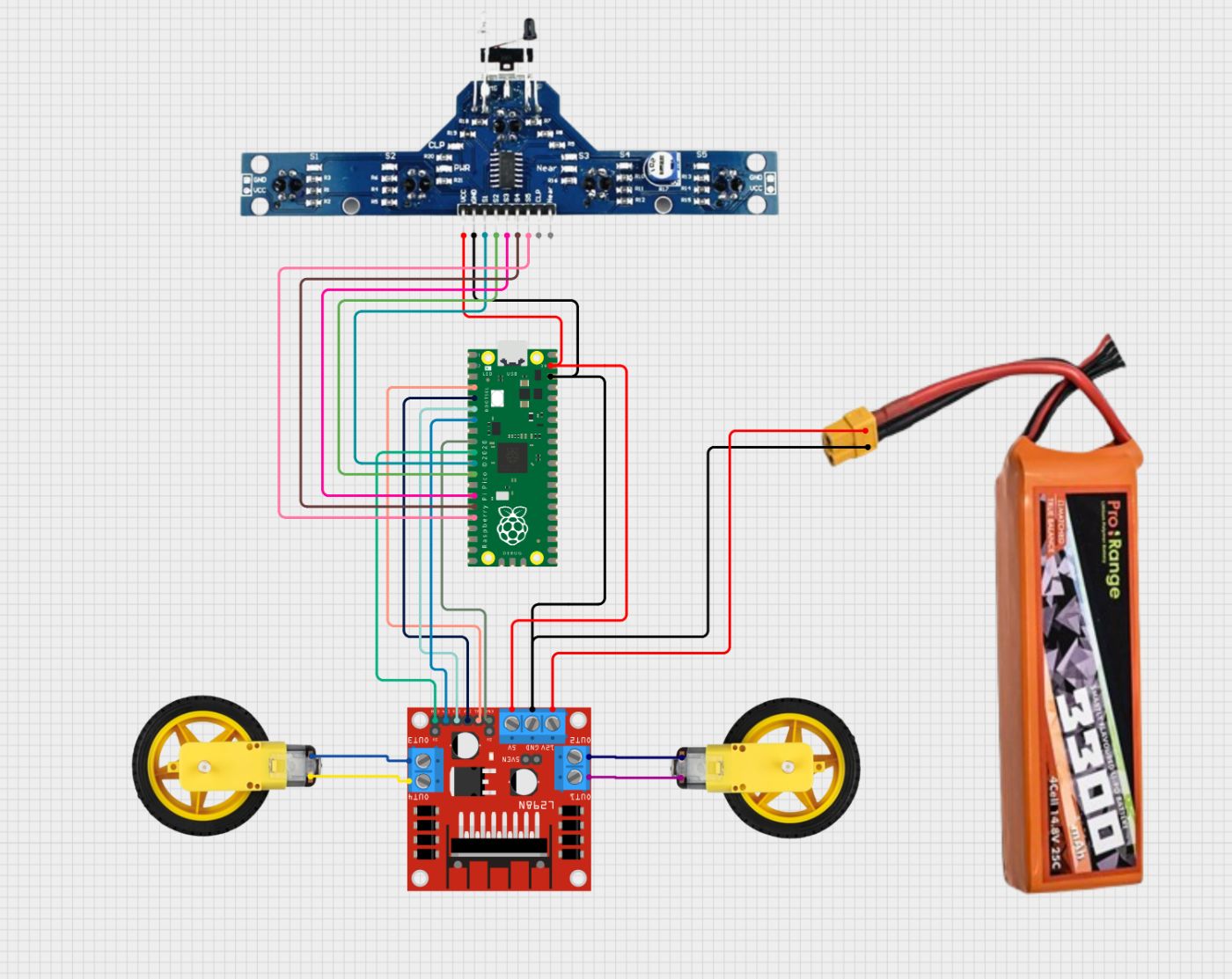
Connection Table
L298N to Pico
| L298N Pin | Connects To |
|—-|—-|
| IN1 | Pico GP2 |
| IN2 | Pico GP3 |
| IN3 | Pico GP4 |
| IN4 | Pico GP5 |
| ENA | Pico GP6 (PWM) |
| ENB | Pico GP7 (PWM) |
| VCC | 12V from the battery |
| GND | Pico GND & battery GND |
| 5V | V_Sys pin |
BFD 1000 to Pico
| IR Sensor Pin | Connects To (Pico Pin) | Function |
|—-|—-|—-|
| OUT1 | GP8 | Left-most sensor |
| OUT2 | GP9 | Left sensor |
| OUT3 | GP10 | Center sensor |
| OUT4 | GP11 | Right sensor |
| OUT5 | GP12 | Right-most sensor |
| VCC | 5V | Power |
| GND | GND | Ground |
IR Sensor Calibration
-
Run your line follower code in Thonny.
-
You should see values being printed in the following format corresponding to each sensor:-
Sensors: [x, x, x, x, x] -
Place the bot on a white surface. You should see:
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1](white reflects IR = HIGH). -
Move the centre sensor over the black line. You should see:
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1](black absorbs IR = LOW). -
Slide the bot side to side across the line. All sensors should detect black (
0) when over a line. -
Adjust potentiometers (if needed) on the IR sensor for reliable
0/1switching.
Test Run Video
Drive Link:-https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ODuU0T4gvLMk8YIl7x5UDorZBtHX7OeK/view?usp=sharing
That’s all, folks, for this project
Meet you in another tutorial like this
Thanks,
Shivank Dan